OVERVIEW
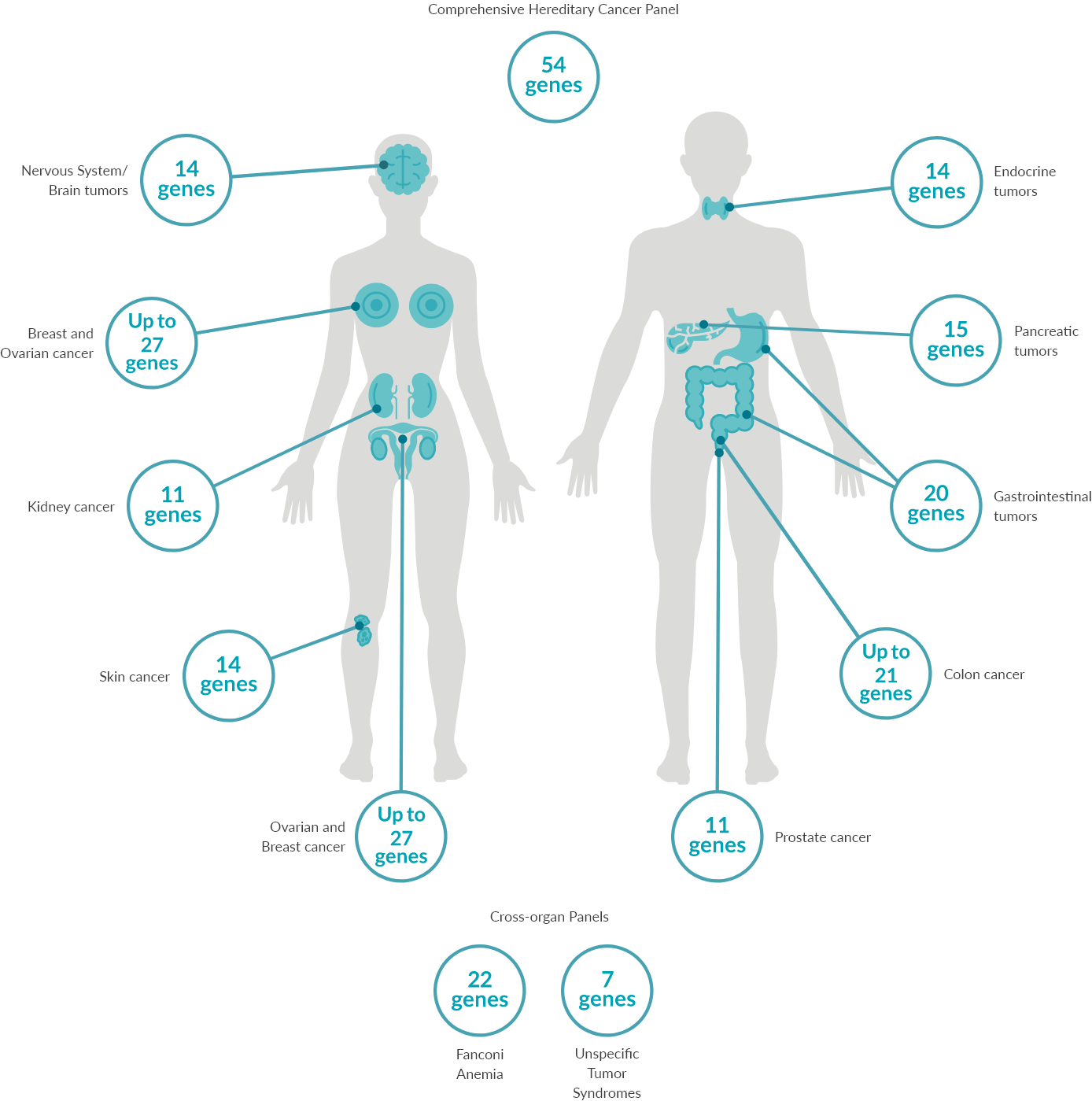
Predict90-95% of most cancers occur sporadically without an inherited genetic cause. 5-10% are associated with a genetic cause, for which we offer 14 separate gene panels covering >30 cancer types spanning across >10 organs and one large targeted comprehensive panel that includes 54 genes associated with many cancer types.
The outcome of the test can be a risk estimation of developing cancer from a genetic cause.
Estimating the risk of developing hereditary cancer provides the person a chance to be proactive about their health by taking preventative measures and/or undergoing routine monitoring.

*Our tests can be ordered through our local partners. Please choose one of the locations listed below.
1 ml EDTA Blood
Please note: DO NOT FREEZE. Ship with a frozen ice pack. Prepare the package such that the tube is tightly packed and not loose. Avoid getting the blood tube wet from the ice pack. Place a paper towel in between ice pack and blood tube if necessary. In sub-zero temperatures, include an unfrozen ice pack in the shipping container as insulation.
15-25 working days
DNA is isolated and next generation sequencing is performed on all coding exons and conserved intronic regions. Single base pair changes, small deletions and duplications and copy number variants (CNV) are identified. Sequencing runs result in a Quality Score of >30 (accuracy >99.9%) in at least 75% of all bases with a coverage of >20-fold. CNV detection sensitivity is 76.99% and precision is 62.59% (with GC limitation between 0.4 and 0.6 per target sensitivity is 77.04% and precision is 84.10%). Variant classification is performed following ACMG guidelines (Richards et al. 2015, Genet Med 17:405; Kearney et al. 2011, Genet Med 13:680).
Next generation
sequencing (Illumina)
Twist Human Core
Exome plus Ref Seq
Spikeln
Illumina DRAGEN
Bio-IT Platform
VarSeq by
GoldenHelix
hg38, NCBI GR38
>30 (precision >99,9%)
in min. 75% of bases
99.92-99.93%; confirmation of reported SNV with Sanger
sequencing, data analysis with
SeqPilot
Richards et al. 2015, Genet Med
17:405; Ellard et al. “ACGS Best
Practice Guidelines for Variant
Classification 2020″
MaxEntScan,
SpliceSiteFinder-like,
REVEL
HGMD Professional
release, ClinVar,
gnomAD

POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE TEST
A diagnostic report outlining the results of the sequencing analysis.
Changes in DNA sequences (variants) can be detrimental and eventually lead to cancer development. Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in cancer-associated genes are reported.
Please note that if pathogenic variants are not identified, this does not preclude the possibility of developing cancer from unknown genetic factors or sporadic causes.