OVERVIEW
WHAT IS EVARTIA?Evartia metabolic test screens for genetic mutations in people suspected of having an inherited metabolic disease. Evartia covers the major categories of inherited metabolic diseases and is offered as a single, detailed panel of 223 genes involved in metabolic pathways. It is based on ‘Target Capture Enrichment Technology’, a technology developed in-house by our team of experts.
Defects in metabolic genes disrupt the actions of the metabolic pathways they are involved in, leading to either toxic accumulation of substances or deficient production of important enzymes and proteins. These can cause a variety of symptoms, that usually manifest shortly after birth or within weeks of birth; but they could also progress slowly over the years and appear in infancy, childhood, adolescence, early or late adulthood. Symptoms and metabolic episodes can also be triggered by specific foods or medications, dehydration, minor illness, sweat or other factors, which would necessitate urgent, appropriate action.
The variability of symptoms and the complexity of detecting metabolic diseases, especially in adult patients, makes identifying a metabolic disorder complicated and time-intensive. Evartia is a comprehensive and reliable test that can help uncover the cause of persistent, debilitating symptoms through genetic testing. Identification of the disease-causing variant can help patients receive the appropriate and essential treatment that can markedly improve or reduce their symptoms, benefiting their quality of life.
Being a single, comprehensive panel, Evartia can:
• Identify complex diseases with a wide spectrum of symptoms and age of onset faster
• Reduce the need for complex and invasive tests
• Lead to the most effective or contraindicated therapies
• Lead to accurate prognosis
• Reduce symptoms and chronic complications, revert disease progression with appropriate therapy
• Allow for taking informed decisions on the best clinical management for the affected individual
• Lead to early diagnosis of other family members

WHO IS EVARTIA FOR?
Patients with common symptoms of a metabolic disease
Patients with a spectrum of overlapping symptoms that vary in age of onset and severity
Patients with neurological symptoms that haven’t improved with routine therapies
Individuals with a family history of a metabolic disease
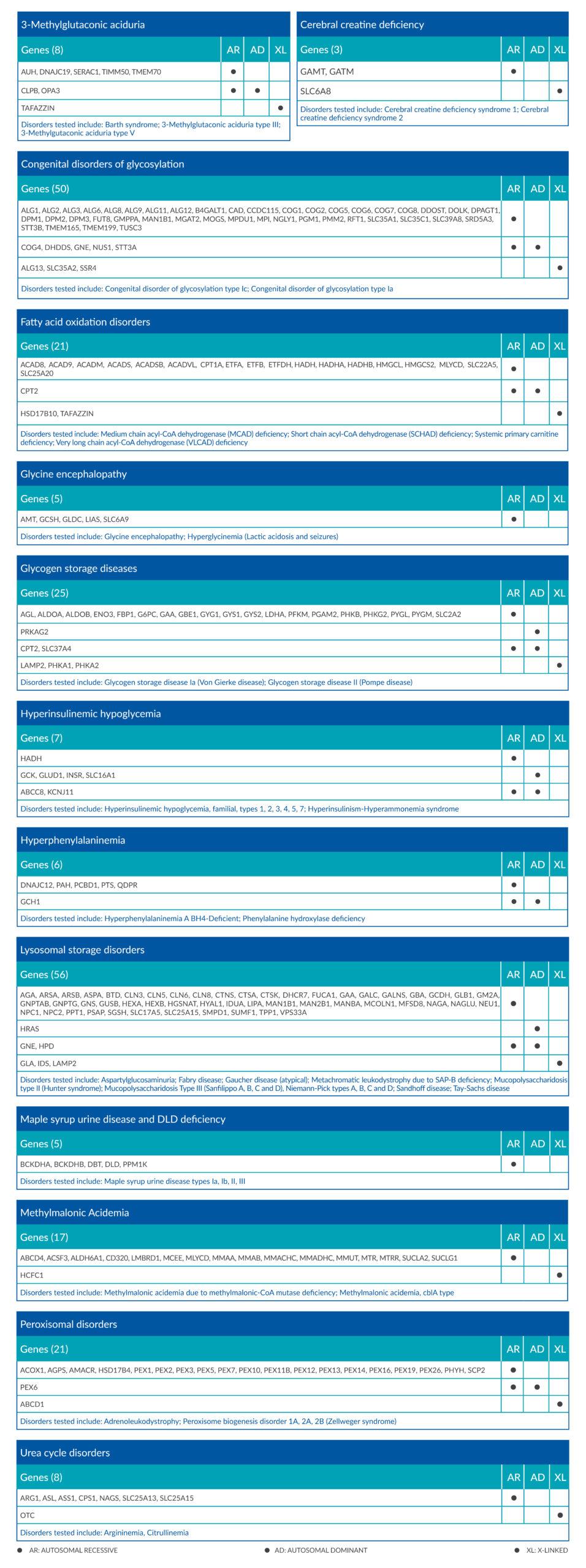
To facilitate the detection process, Evartia metabolic test covers the major classes of inherited metabolic diseases and is offered as a single, detailed panel of 223 genes involved in metabolic pathways.
The genetic alterations tested in Evartia include single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions and deletions (Indels) and copy number alterations (CNAs).
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANTAGES
TARGETED TECHNOLOGY
Evartia is based on a novel, target capture enrichment technology that has been thoroughly validated for its accuracy and precision.

FULL EXONIC COVERAGE
Evartia screens for all coding regions* on the genes tested, examining single nucleotide variants, small insertions and deletions and copy number variants down to single exon resolution.
*Exceptions apply – see technology section for details
INNOVATIVE BIOINFORMATICS
Innovative bioinformatics pipelines analyze the sequencing data produced from each sample, increasing the sensitivity and specificity of Evartia.

WHY CONSIDER GENETIC TESTING?
METABOLIC DISORDERS ARE UNDER-RECOGNIZED AND UNDER-DETECTED
Traditionally regarded as ‘childhood diseases’, the prevalence of adults with metabolic disorders who are undetected is unknown. Metabolic diseases have a range of symptoms and age of onset, and no specific phenotype. Also, they may have overlapping symptoms with neurologic, psychiatric or cardiovascular disorders. Without treatment, they can get progressively worse, cause acute pain, and chronic, irreversible complications.
The path towards identifying a metabolic disease hasn’t been straightforward. If a patient with a metabolic disease is not identified through newborn screening, due to the metabolic disease not being a part of the diseases tested or due to technological limitations, detection depends on the time of symptom onset. This can be anytime from infancy, childhood, adolescence or adulthood . Often, patients have to undergo lengthy and complicated biochemical or enzymatic testing which includes a variety of specimen types such as blood, urine or sweat. Additionally, invasive biopsies from muscle or cerebrospinal fluid may be needed.
With Evartia, you are one genetic test away from taking informed, accurate, and early decisions on the best clinical management.
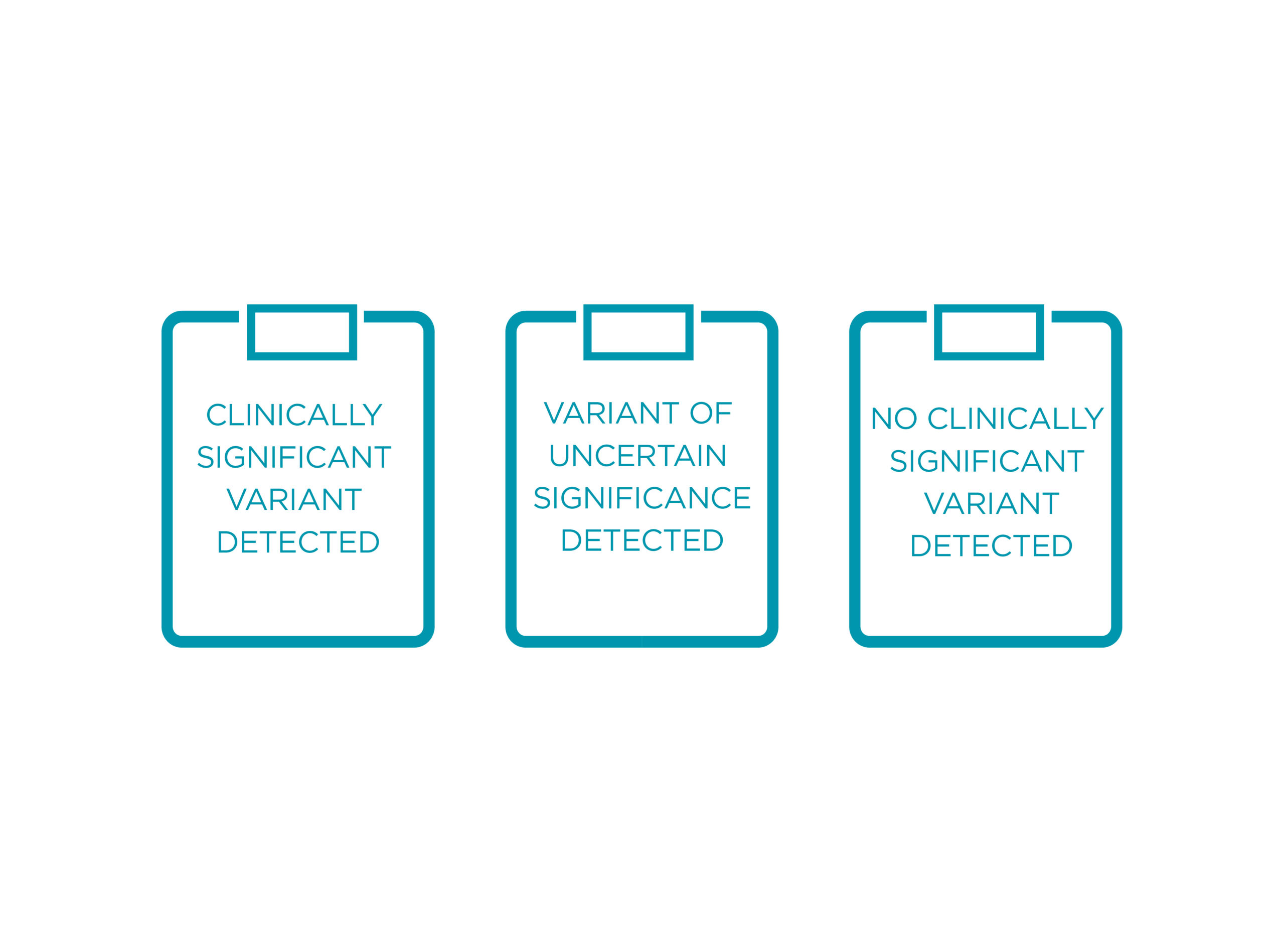
POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE TEST
The Evartia report will have information on the following:
• Results on genes tested
• Thorough interpretation and clinical significance of mutations detected
Evartia reports on clinically significant and no clinically significant variants, as well as variants of uncertain significance.