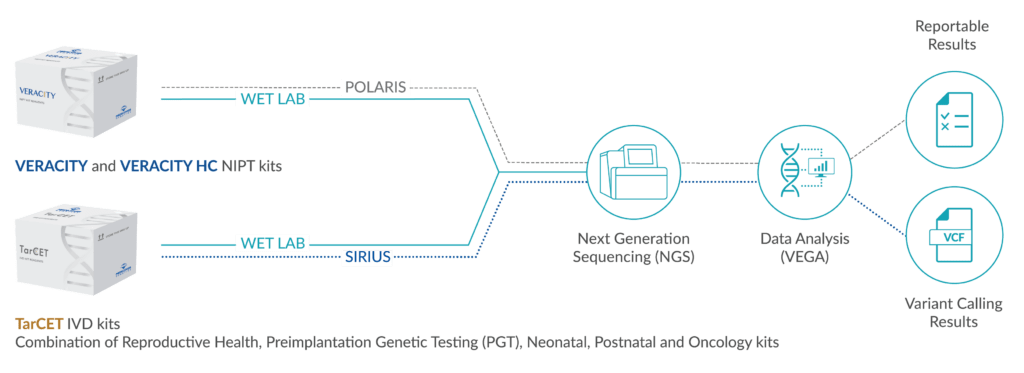
OVERVIEW
DETECTClose to 20 million new cancer cases and 10 million deaths have occurred annually in recent years. Solid tumors represent ~90% of adult cancers and millions of histopathology slides are analyzed annually revealing information crucial for cancer diagnosis and staging. In up to 40% of patients, complex genomic alterations are identified which can serve as biomarkers to predict response to a specific therapy and/or prognosis.
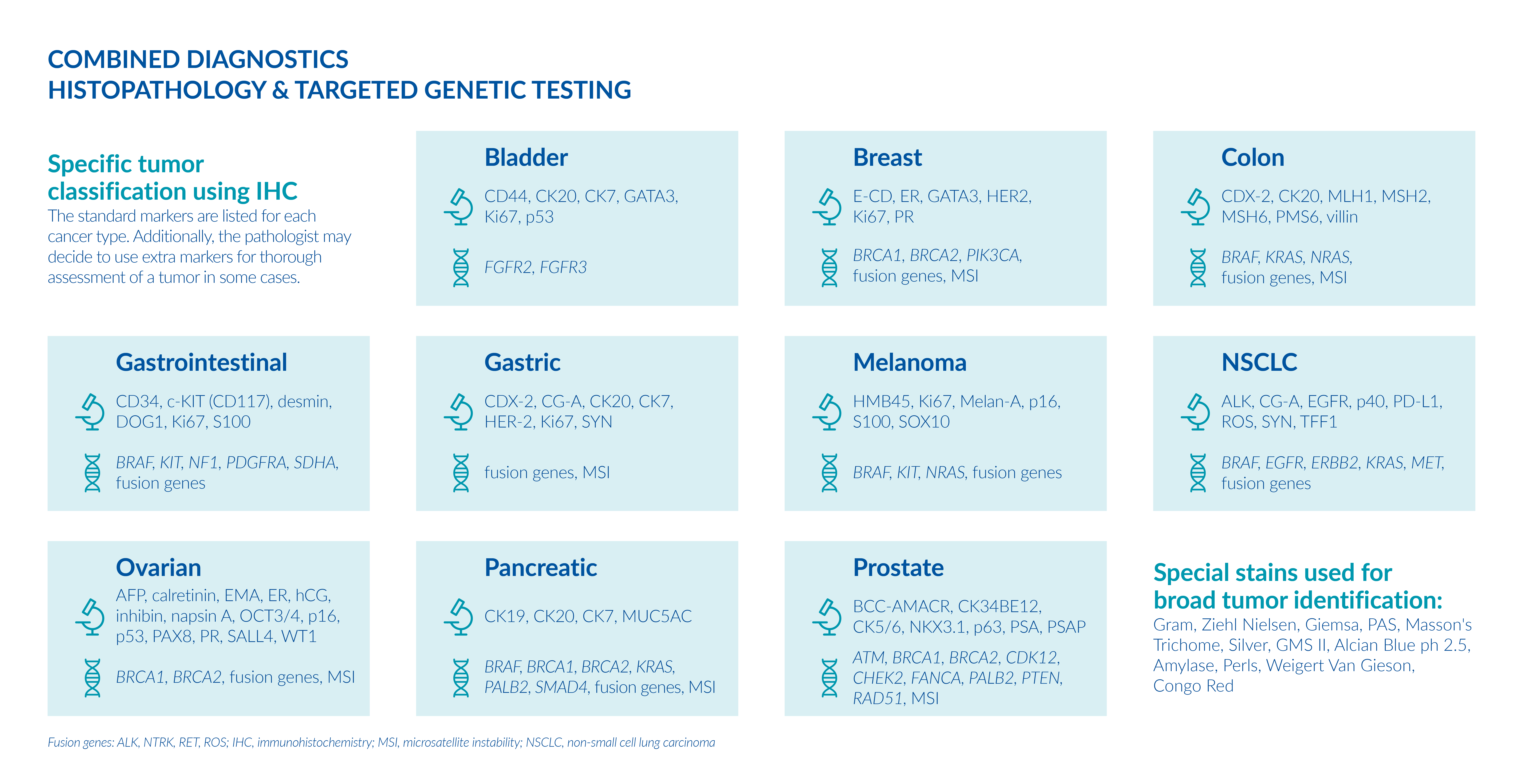
Histopathological examination and genetic testing can determine the tumor profile and suggest appropriate management or treatment plans, when available. We offer both histopathology and molecular genetic analyses for solid tumors.
Characterizing the cellular and molecular changes in a solid tumor is critical for treatment strategy. Customized treatment depends on the type, severity (stage) and the specific genetic alterations in the tumor tissue. Genotype-directed therapy or genotype-matched clinical trials can improve patient care and survival.

IMPORTANCE OF GETTING TESTED
Histopathology and genetic tumor profiling allow for individualized and more efficient and personalized treatment. Treating a tumor based on its unique cellular and molecular features may result in a better outcome, including improved clinical management and increased survival.

Patients who are diagnosed with
a solid tumor and require
a pathology and/or genetic test analysis
OUR SOLUTION
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Microscopic examination of the tumor sample provides specific information about the type and the stage of the tumor, its location and size and if it has spread to other healthy parts of the body.
GENETIC TESTS
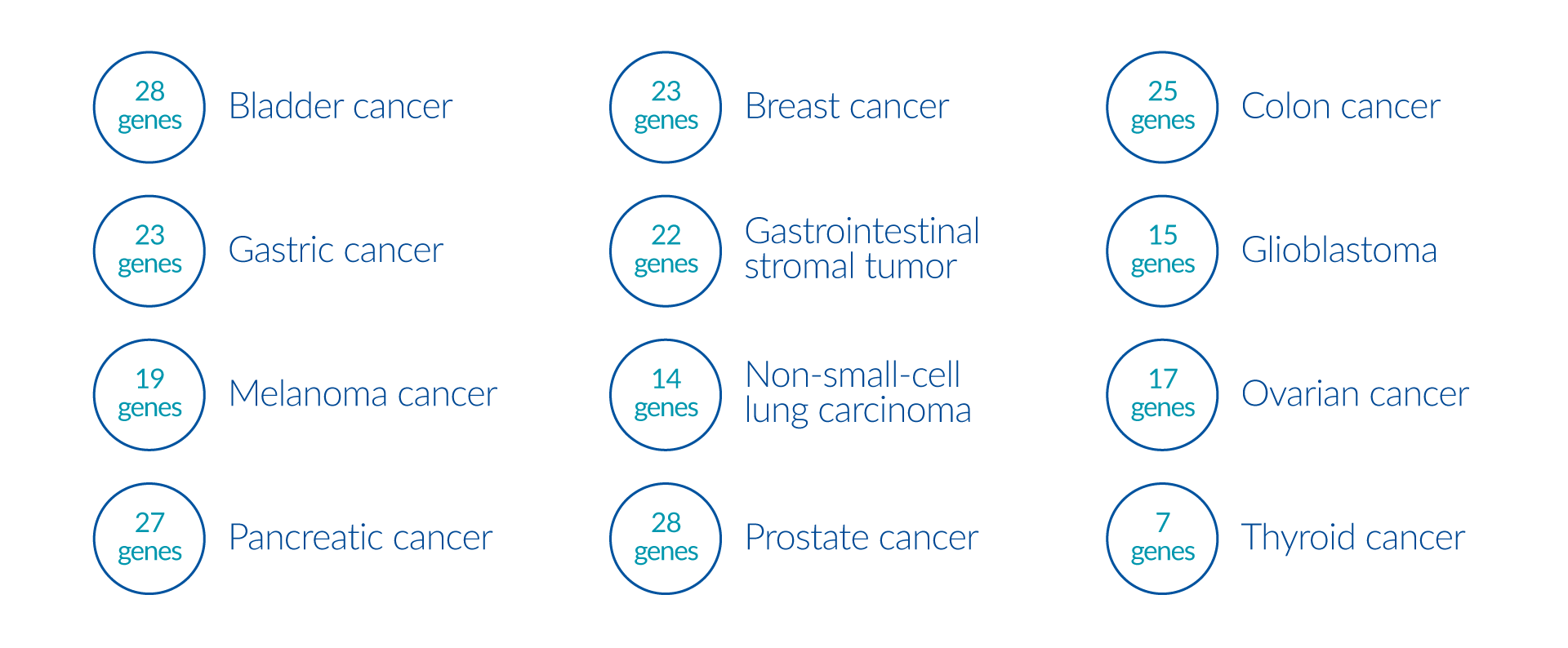
Based on the histopathological findings, genetic analysis may be recommended. Your physician can choose from individual targeted-therapy tests, gene panels or a single comprehensive gene panel.
Consider Hereditary Cancer Panels Predict&Prevent if your patient’s tumor has a genetic cause
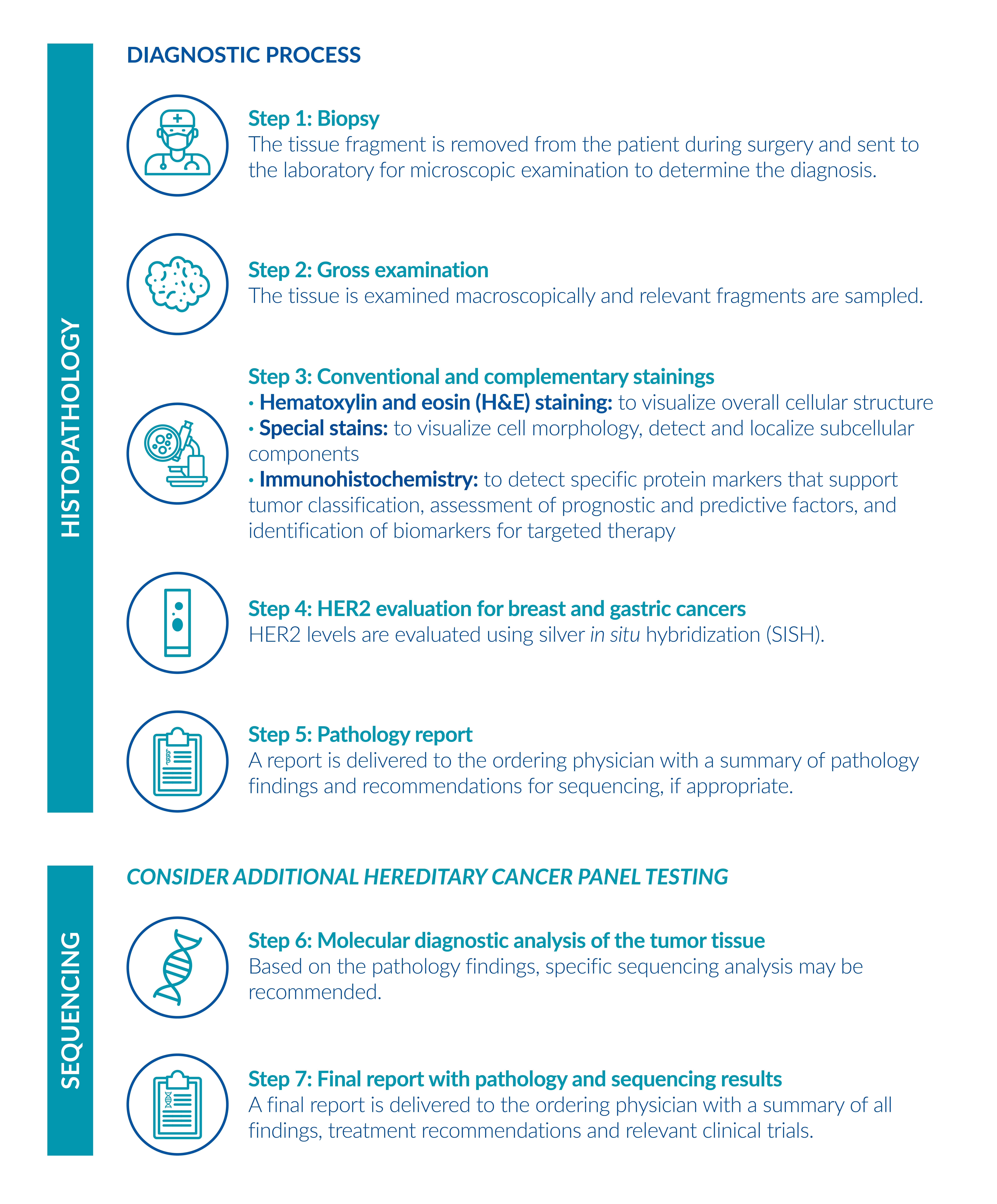
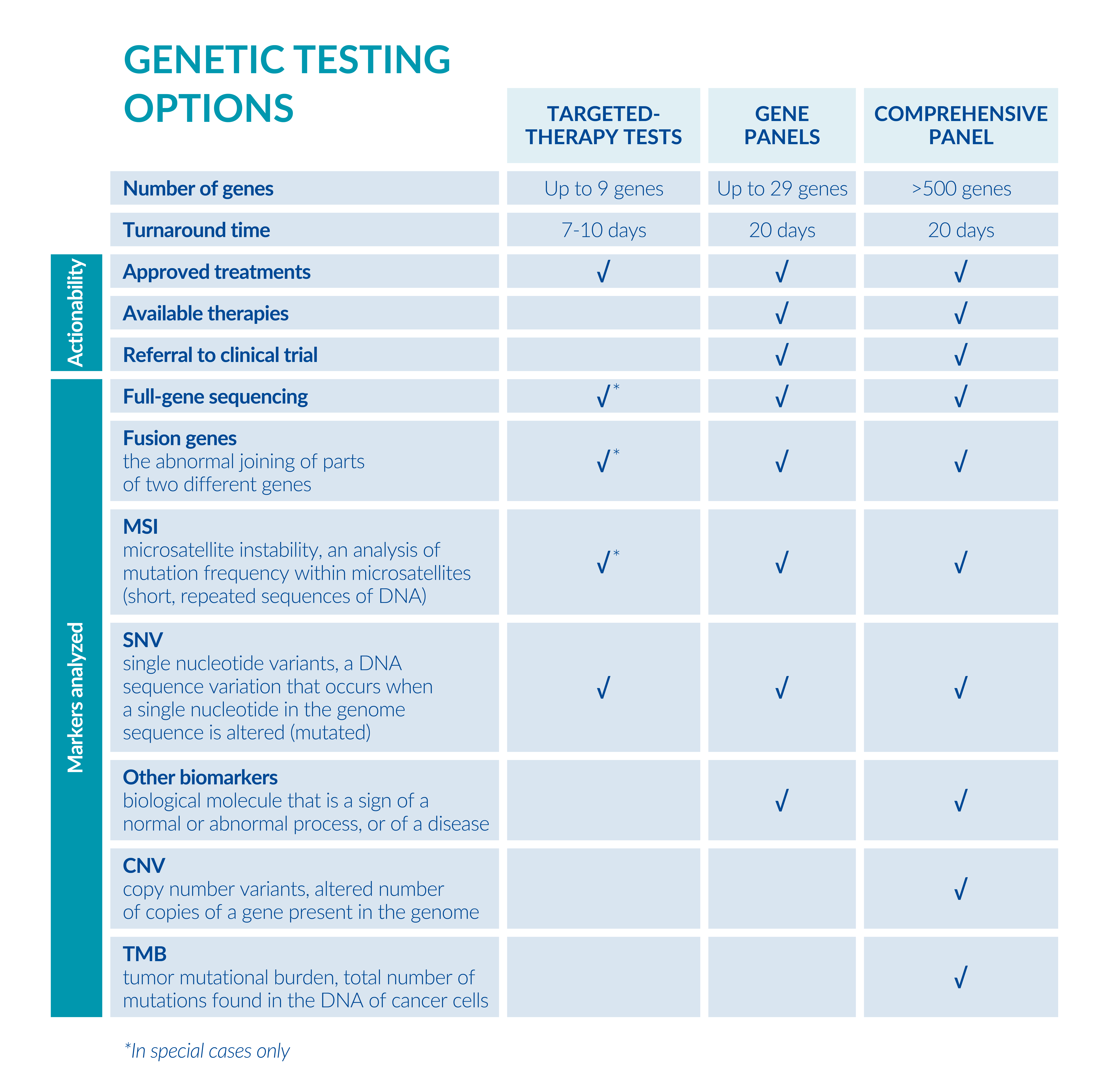
TEST OPTIONS
GENETIC TESTING only
● Targeted-Therapy Tests
● Gene Panels
● Comprehensive Panel
By combining histopathology and genetic testing, you can receive a complete diagnosis of the tumor which will guide your physician to decide on the most appropriate treatment for you, as well as recommend clinical trials that can help improve the clinical outcome.
Identifies specific genomic changes that are relevant to therapy with approved therapeutic products (targeted therapies)
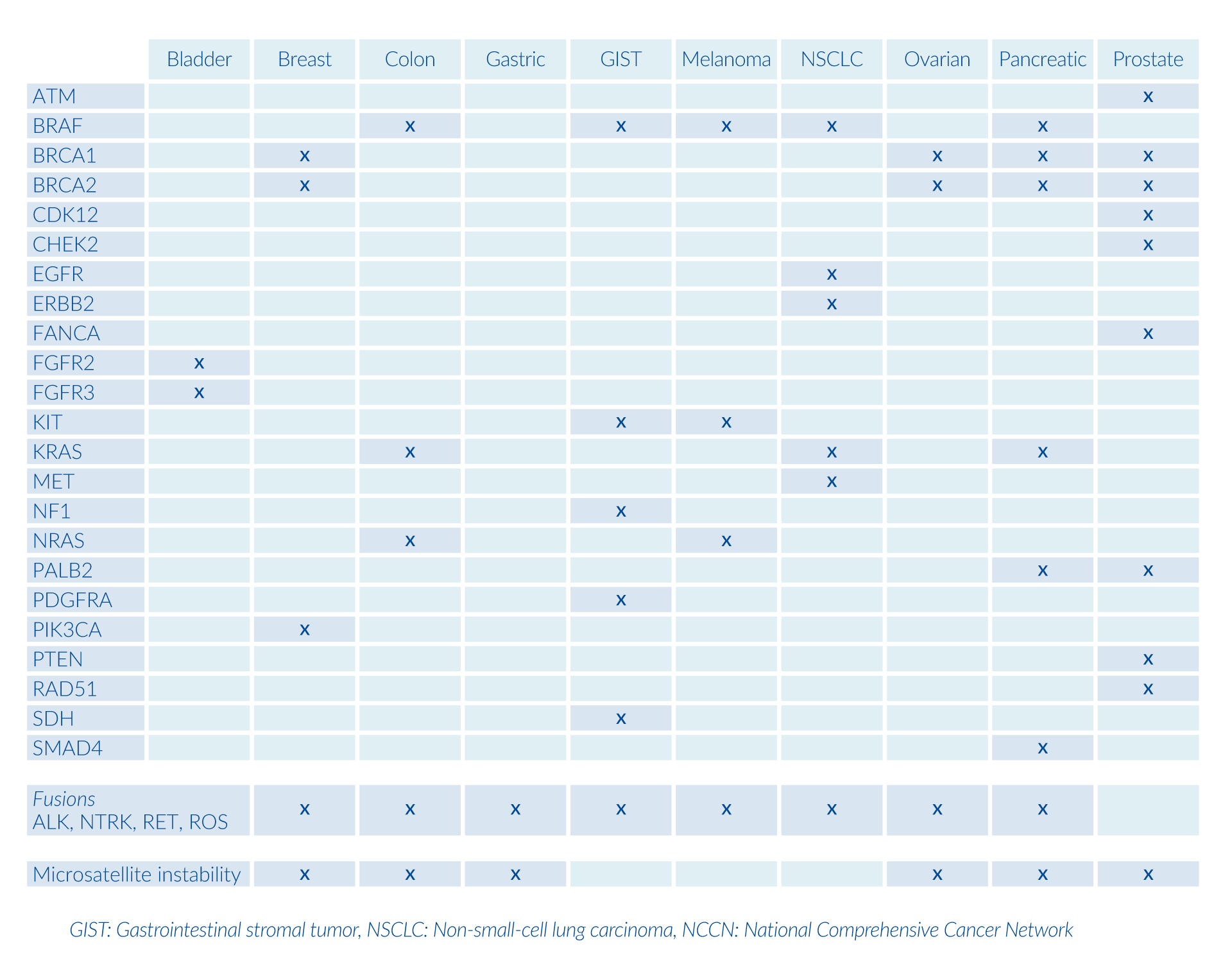
By analyzing >500 genes, this panel provides a complete molecular profile of the tumor by investigating genomic mechanisms involved in tumor formation, including microsatellite instability and tumor mutation burden analysis. This panel is recommended for patients with cancer of unknown primary origin and other rare cancers. The analysis also includes:

In addition to targeted therapies, gene panels can identify additional biomarkers, microsatellite instability, and recommend clinical trials.
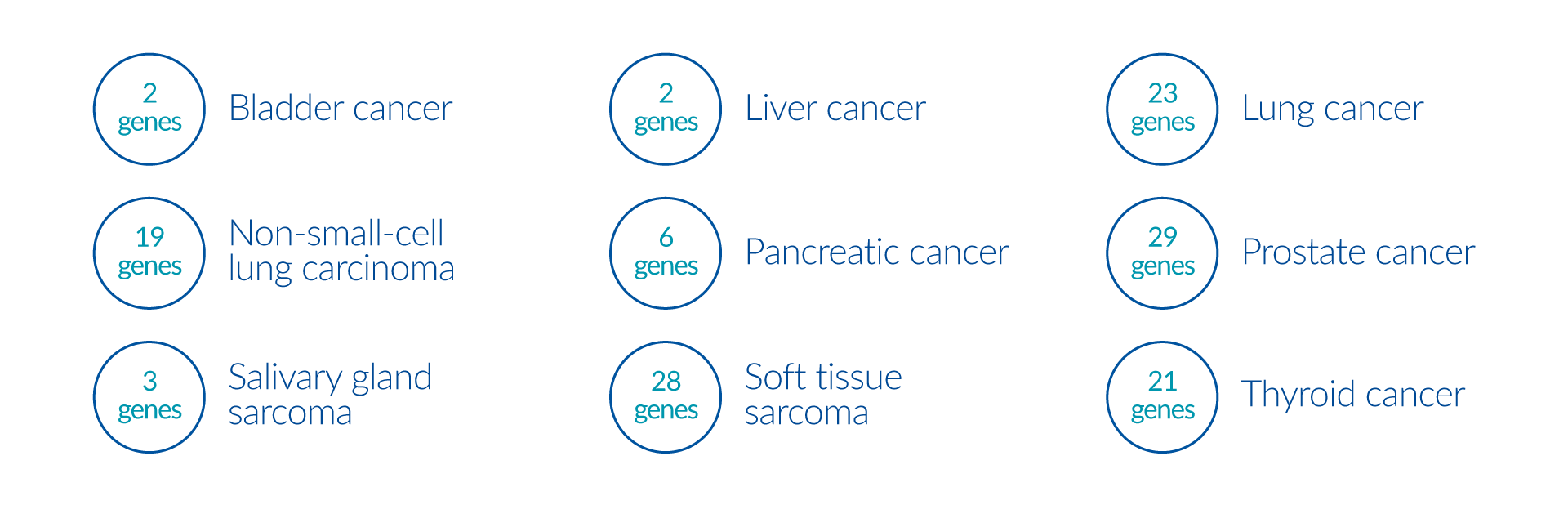
Fusion gene panels may provide clinically useful information that impact diagnosis, prognosis, or therapy of the associated tumors.

POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE TEST
A diagnostic report outlining the results of the histopathology and/or the sequencing results from genetic testing is provided.
Pathology report includes macroscopic and microscopic descriptions of the provided sample, results of all tests conducted, and conclusions based on the final histopathological diagnosis. Conclusions include classification of lesions, WHO disease code, and recommendations, with the suggestion to perform sequencing analyses included if necessary.
Sequencing report includes changes in DNA sequence (variants) including single nucleotide variants, copy number variants (only for comprehensive panel) and fusion genes, as well as tumor mutational burden and microsatellite instability, as well as the effect on carcinogenesis. Possible therapy options and clinical trials relevant to the patient’s location will be listed.
Targeted-therapy analysis, solid tumor panels and the comprehensive tumor panel are covered as part of the sequencing report where applicable.
Targeted-therapy analysis identifies specific genomic changes that are relevant to therapy with approved therapeutic products (targeted therapies).
Solid tumor panels and comprehensive tumor panel may identify additional genomic findings that are not prescriptive or conclusive for use of any targeted therapies. Use of these panels does not guarantee a patient will be matched to a treatment. A negative result does not rule out the presence of an alteration.
MEDICAL GENETIC COUNSELLING
We provide expert medical genetic counselling as part of a genetic testing journey. Genetic counselling is a process of communication that supports patients and their relatives before and after genetic testing. It is educational, impartial and nondirective. Prior to any genetic test, genetic counsellors will obtain a detailed family history, explain the method of testing that will be used, its risks and benefits, the limitations of the diagnosis and the implications of making a genetic diagnosis (Elliott and Friedman, 2018, Nat Rev Genet 19:735).
Upon receiving the genetic test results, genetic counselling can help the specialist physician and the patient to interpret them. They can be advised of the consequences of the results including the probability of developing the genetic disorder or passing it on to children, as well as ways to prevent, avoid or reduce these risks (Yang and Kim, 2018, Ann Lab Med 38:291). Our goal of counselling is to provide the patient with greater knowledge and thus, a better understanding of the results and the ability to make a more informed decision.

Tissue fragments from a biopsy:
– Stored in 10% formalin (stable for 24-72 hrs)
– Embedded in paraffin blocks (stored in dry and dark conditions)
Histopathology analysis: 7-10 working days
Genetic analysis: 7-20 working days
Information updated soon
OUR TESTS
Genes: AKT1, APC, ARID1A, ATM, CDKN2A, CREBBP, E2F3, EP300, ERBB2, ERCC2, FANCC, FGFR2, FGFR3, HRAS, KDM6A, KRAS, MDM2, MSH2, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PTCH1, PTEN, RB1, STAG2, TERT, TP53, TSC1; Fusion Genes: FGFR3-BAIAP2L1, FGFR3-TACC3
Genes: AKT1, ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CCND1, CHEK2, ERBB2, FAT1, FGFR1, MDM2, MYC, NF1, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PALB2, PIK3CA, PTEN, RAD51C, RB1, STK11
Genes: AKT1, ALK, APC, ATM, BRAF, EPCAM, ERBB2, JAK1, KRAS, MET, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, NRAS, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PIK3CA, PMS2, PTEN, RET, ROS1, STK11, TP53
Genes: ATM, BMPR1A, BRCA1, BRCA2, CDH1, EGFR, ERBB2, MET, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PIK3CA, PMS2, RET, ROS1, SMAD4
Genes: APC, ARID1A, ARID1B, ATR, BRAF, CBL, CTNNB1, FGFR1, HRAS, KIT, KRAS, MEN1, NF1, NRAS, PDGFRA, PIK3CA, SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD, ZNF217
Genes: ATRX, BRAF, CDKN2A, CDKN2B, EGFR, H3F3A, HIST1H3B, HIST1H3C, IDH1, IDH2, MET, MGMT, PDGFRA, PTEN, TERT, TP53
Genes: Fusion Genes: FGFR2-CCDC6, FGFR2-TACC3
Genes: Fusion Genes: CCDC6-RET, CD74-NRG1, CD74-NTRK1, CD74-ROS1, CRTC1-MAML2, CUX1-RET, EML4-ALK, EZR-ROS1, FGFR3-TACC3, GOPC-ROS1, KIF5B-ALK, KIF5B-RET, KLC1-ALK, LRIG3-ROS1, MPRIP-NTRK1, NCOA4-RET, SDC4-ROS1, SLC34A2-ROS1, SND1-BRAF, STRN-ALK, TFG-ALK, TPM3-ROS1, TRIM33-RET
Genes: BAP1, BRAF, BRCA2, CDK4, CDKN2A, GNA11, GNAQ, GNAS, HRAS, KIT, MAP2K1, MITF, NF1, NRAS, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PTEN, TERT
Genes: ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDK12, CHEK2, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, NBN, PALB2, PMS2, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, STK11
Genes: ALK, APC, ATM, BRAF, BRCA1, BRCA2, CDKN2A, ERBB2, FANCC, FANCG, GNAS, KRAS, MDM2, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PALB2, PIK3CA, PMS2, RET, ROS1, SMAD4, STK11, TP53; Fusion Genes: EWSR1-FLI1, GATM-BRAF, HACL1-RAF1, HERPUD1-BRAF, SND1-BRAF, ZSCAN30-BRAF
Genes: AKT1, AR, ATM, ATR, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDK12, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCA, FANCL, FOXA1, IDH1, MYC, NCOR1, PALB2, PIK3CA, PTEN, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, RB1, SMAD4, SPOP, TP53; Fusion Genes: ESRP1-RAF1, RAF1-ESRP1, SLC45A3-BRAF, SND1-BRAF, TMPRSS2-ERG, UBE2L3-KRAS
Genes: Sarcoma Fusion Gene Panel: NTRK3-ETV6, EWSR1-NR4A3, EWSR1-PBX1, EWSR1-ZNF384, EWSR1-ATF1, EWSR1-PATZ1, EWSR1-DDIT3, EWSR1-SP3, EWSR1-FEV, EWSR1-CREB1, EWSR1-FLI1, EWSR1-ETV4, EWSR1-ETV1, EWSR1-ERG, YY1-EWSR1, EWSR1-ZNF444, EWSR1-SMARCA5, NFATC2-EWSR1, SS18-SSX1, SS18-SSX4, FUS-CREB3L2, FUS-CREB3L1, FUS-DDIT3, FUS-ERG, FUS-ATF1, FUS-FEV; Salivary Gland Sarcoma Fusion Gene Panel: CRTC1-MAML2, ETV6-NTRK3, FGFR1-PLAG1; Soft Tissue Sarcoma Fusion Gene Panel: ASPSCR1-TFE3, ATIC-ALK, CARS-ALK, CLTC-ALK, COL1A1-PDGFB, DCTN1-ALK, ETV6-NTRK3, EWSR1-ATF1, EWSR1-CREB1, EWSR1-DDIT3, EWSR1-ERG, EWSR1-ETV1, EWSR1-ETV4, EWSR1-FEV, EWSR1-FLI1, EWSR1-WT1, FN1-ALK, FUS-DDIT3, NCOA4-RET, PAX3-FOXO1, PAX7-FOXO1, PPFIBP1-ALK, RANBP2-ALK, SEC31A-ALK, SS18-SSX1, SS18-SSX2, TPM3-ALK, TPM4-ALK
Genes: Lung Cancer Fusion Gene Panel: CCDC6-RET, CD74-NRG1, CD74-NTRK1, CD74-ROS1, CRTC1-MAML2, CUX1-RET, EML4-ALK, EZR-ROS1, FGFR3-TACC3, GOPC-ROS1, KIF5B-ALK, KIF5B-RET, KLC1-ALK, LRIG3-ROS1, MPRIP-NTRK1, NCOA4-RET, SDC4-ROS1, SLC34A2-ROS1, SND1-BRAF, STRN-ALK, TFG-ALK, TPM3-ROS1, TRIM33-RET; Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Gene Panel: ALK, BRAF, BRCA1, BRCA2, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, MET, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, PIK3CA, RET, ROS1; Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Fusion Gene Panel: BAG4-FGFR1, CCDC6-RET, CD74-NRG1, CD74-ROS1, EML4-ALK, EZR-ROS1, GOPC-ROS1, HIP1-ALK, KIF5B-ALK, KIF5B-RET, KLC1-ALK, LRIG3-ROS1, SDC4-ROS1, SLC34A2-ROS1, STRN-ALK, TFG-ALK, TPM3-ROS1, TPR-ALK, TRIM33-RET; Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Targeted Panel: BRAF, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, MET, NTRK1/2/3 fusion