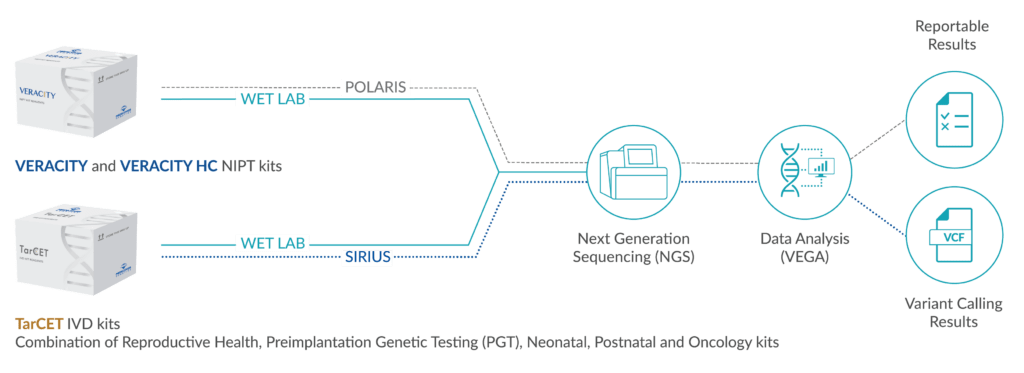
Scientific background
- 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type III (OPA3, AR)
- 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria, type V (DNAJC19, AR)
- Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency (AMACR, AR)
- Anemia, sideroblastic, with ataxia (ABCB7, XL)
- Ataxia telangiectasia (ATM, AR)
- Ataxia telangiectasia-like disease (MRE11, AR)
- Ataxia, autosomal recessive (PEX10, AR)
- Ataxia, cerebellar, Cayman type (ATCAY, AR)
- Behr syndrome (OPA1, AR)
- Biotinidase deficiency (BTD, AR)
- Boucher-Neuhauser syndrome (PNPLA6, AR)
- CAPOS syndrome (ATP1A3, AD)
- Cerebellar ataxia (CP, AR)
- Cerebellar ataxia and mental retardation (CA8, AR)
- Cerebellar ataxia and mental retardation 4 (?) (ATP8A2, AR)
- Cerebellar ataxia with spasticity (GBA2, AR)
- Cerebellar ataxia, deafness and narcolepsy, autosomal dominant (DNMT1, AD)
- Cerebellar hypoplasia and mental retardation (VLDLR, AR)
- Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CYP27A1, AR)
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-dominant, 1 (GJB1, XLD)
- Epilepsy, progressive, myoclonic 6 (GOSR2, AR)
- Gaucher disease type III (GBA, AR)
- Infantile-onset limb and orofacial dyskinesia (PDE10A, AR)
- Joubert syndrome phenotype (POC1B, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 1 (INPP5E, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 10 (OFD1, XLR)
- Joubert syndrome type 11 (TTC21B, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 12 (KIF7, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 13 (TCTN1, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 14 (TMEM237, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 15 (CEP41, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 16 (TMEM138, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 17 (CPLANE1, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 18 (TCTN3, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 19 (ZNF423, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 2 (TMEM216, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 20 (TMEM231, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 21 (CSPP1, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 22 (PDE6D, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 23 (KIAA0586, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 3 (AHI1, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 4 (NPHP1, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 5 (CEP290, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 6 (TMEM67, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 7 (RPGRIP1L, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 8 (ARL13B, AR)
- Joubert syndrome type 9 (CC2D2A, AR)
- Joubert/Meckel syndrome phenotype (TCTN2, AR)
- Joubert/nephronophthisis phenotype (ATXN10, AR)
- Krabbe disease (GALC, AR)
- Leukoencephalopathy with ataxia (CLCN2, AR)
- Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal involvement and lactate elevation (DARS2, AR)
- Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome (SIL1, AR)
- Metachromatic leukodystrophy (ARSA, AR)
- Mitochondrial recessive ataxia syndrome (POLG, AR)
- Neurodegeneration with iron accumulation in the brain (PLA2G6, AR)
- Neurodegeneration with iron accumulation in brain 1 (PANK2, AR)
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 5 (CLN5, AR)
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 6 (CLN6, AR)
- Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (NPC1, AR)
- Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (NPC2, AR)
- Peroxisome biogenesis defect 5B (PEX2, AR)
- Polymicrogyria, bilateral frontoparietal (ADGRG1, AR)
- Polyneuropathy, ataxia, hearing loss, retinitis pigmentosa and cataract (ABHD12, AR)
- Posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa (FLVCR1, AR)
- Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency type 4 (COQ8A, AR)
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 deficiency (DLAT, AR)
- Salla disease (SLC17A5, AR)
- Spastic ataxia (POLR3A, AR)
- Spastic ataxia (SPG7, AR)
- Spastic ataxia type 1 (VAMP1, AD)
- Spastic ataxia type 2 (KIF1C, AR)
- Spastic ataxia type 3 (MARS2, AR)
- Spastic ataxia type 4 (MTPAP, AR)
- Spastic ataxia type 5 (AFG3L2, AR)
- Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguena type (SACS, AR)
- Spastic paraplegia 76 (CAPN1, AR)
- Wolfram syndrome (WFS1, AR)
Disorders are inherited in an autosomal dominant (AD), autosomal recessive (AR), X-linked (XL), or X-linked dominant (XLD) pattern.
For detailed information on ataxias and diagnostics, please visit our overview page ATAXIAS.