OVERVIEW
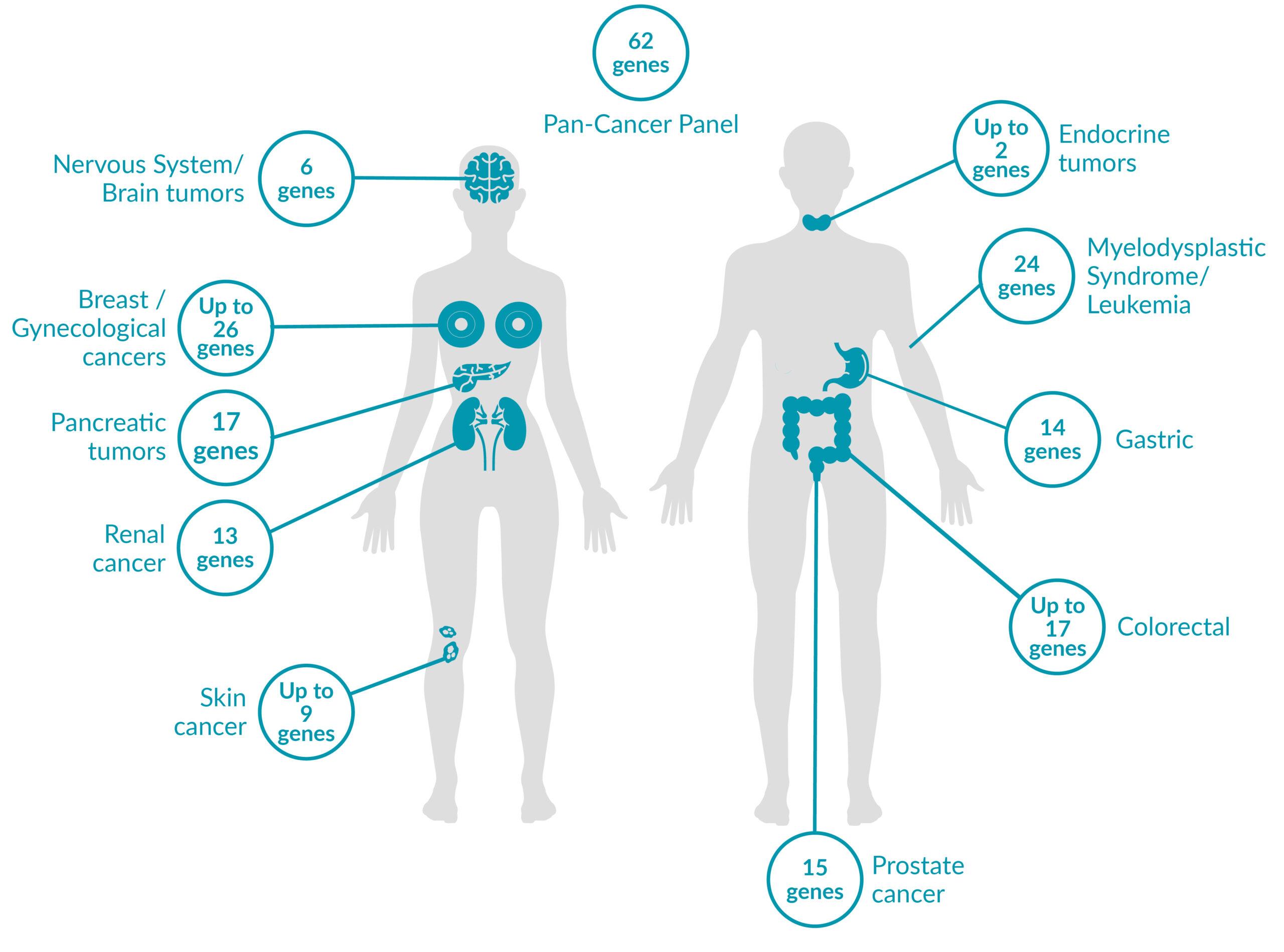
WHAT IS PreSENTIA?PreSENTIA is a genetic test that can identify genetic variants which are associated with cancer susceptibility and run in the families. It offers an extensive portfolio of 19 hereditary cancer panels and can test for up to 62 genes. PreSENTIA can also identify genetic variants responsible for up to 24 hereditary cancer predisposing syndromes.
PreSENTIA uses our novel technological platform which combines our in-house developed Target Capture Enrichment Technology along with our proprietary bioinformatic pipelines. This ensures high-read depth of clinically actionable genes of interest while identifying genetic alterations such as single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions and deletions (INDELs) and copy number alterations (CNAs) with high sensitivity and accuracy.

*Our tests can be ordered through our local partners. Please choose one of the locations listed below.
Buccal swab collection device, which is provided in the PreSENTIA kit
2-3 weeks from sample receipt in our laboratory
gDNA is extracted using a standardized methodology and subjected to mechanical fragmentation prior to DNA library preparation. DNA enrichment for the genomic regions of interest is carried out using a solution-based hybridization method, followed by next generation sequencing (NGS). Single nucleotide variants, small insertions and deletions (≤50bp), and copy number variations (CNVs) are reported. All positive CNVs are confirmed using an orthogonal method. The test aims to detect all coding exons, of MANE and/or Canonical transcripts, and 20bp of adjacent intronic sequence.
Exceptions may include: regions containing repeats, sequences of high homology such as segmental duplications and pseudogenes, as well as regions of extreme GC-content.
Variants are classified according to the criteria set by the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Classification and interpretation of variants is performed using the Varsome Clinical platform, and is according to the published knowledge at the time of testing.
Next generation sequencing (Illumina)
Proprietary Target Capture Enrichment Technology (Click here to see our Publications)
GATK and Vardict variant callers. Targeted CNV calling using a proprietary bioinformatics pipeline utilizing a circular binary segmentation algorithm
Varsome Clinical by Saphetor
hg19, NCBI GRCh37
≥Q30, 99.9% base call accuracy in >80% of the bases.
Minimum percentage of bases with RD greater than 20X = 98%
Sensitivity: 100% (95%CI:94-100%)
Specificity: 100% (95%CI:99.999-100%)
Richards et al. 2015 (1)
Tavtigian SV et al. 2020 (2)
Pejaver V et al. 2022 (3)
ALoFT, BayesDel, DEOGEN2, Eigen, Eigen-PC, FATHMM, FATHMM-XF, FATHMM-MKL, fitCons, LIST-S2, LRT, M-CAP, MetaLR, MetaRNN, MetaSVM, MPC, MutationAssessor, MutationTaster, MutPred, MVP, Polyphen-2, PrimateAI, PROVEAN, REVEL, SIFT, SIFT4G, dbscSNV
More than 100 datasets including ClinVar, gnomAD, ExAC, ClinGen, DECIPHER, etc
(1) Richards et al. 2015, Genet Med 17:405; ClinGen Sequence Variant Interpretation Recommendation for PM2-Version 1.0
(2) Tavtigian SV et al. 2020, Hum Mutat 41(10); Fitting a naturally scaled point system to the ACMG/AMP variant classification guidelines
(3) Pejaver V et al. 2022, bioRxiv; Evidence-based calibration of computational tools for missense variant pathogenicity classification and ClinGen recommendations for clinical use of PP3/BP4
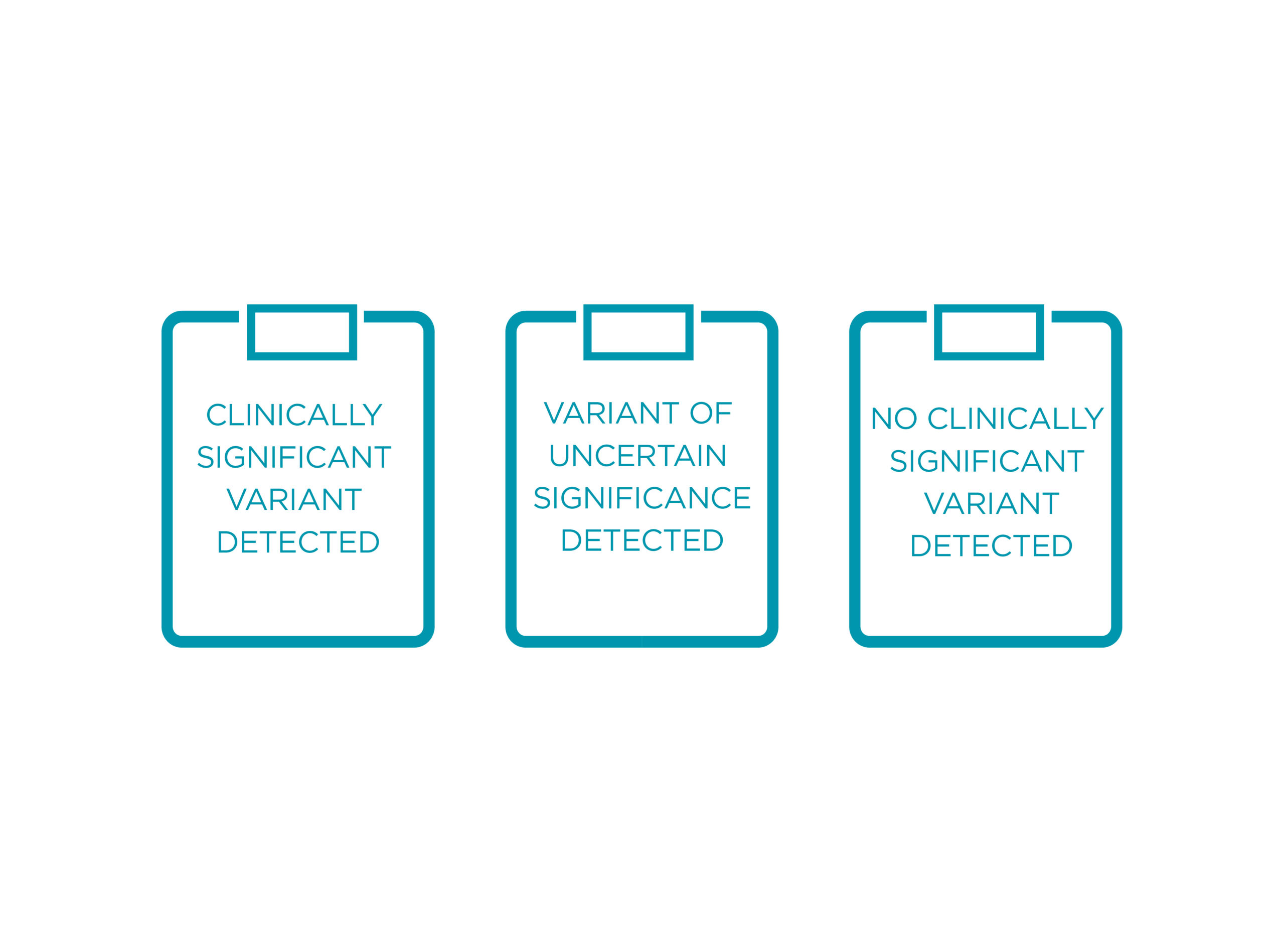
POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE TEST
The PreSENTIA report will have information on the following:
• Results on genes tested
• Thorough interpretation and clinical significance of mutations detected
PreSENTIA reports on clinically significant and no clinically significant variants, as well as variants of uncertain significance.